Peritoneal Dialysis
Peritoneal dialysis (PD) is another form of dialysis modality for the patients with kidney failure. It is widely accepted and effective. It is the most common method of dialysis done at home.
What is peritoneal dialysis?
- The peritoneum is a thin membrane that lines the inner surface of the abdominal cavity.
- The peritoneal membrane is a natural semi-permeable membrane which allows waste products and toxins in the blood to pass through it.
- Peritoneal dialysis is a process of purification of blood through the peritoneal membrane.
What are the types of peritoneal dialysis?
Types of peritoneal dialysis:
- Intermittent Peritoneal Dialysis (IPD)
- Continuous Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis (CAPD)
- Continuous Cycling Peritoneal Dialysis (CCPD)
1. Intermittent Peritoneal Dialysis (IPD)
Intermittent peritoneal dialysis (IPD) is a valuable and effective dialysis option for short term dialysis in hospitalized patients with acute kidney failure, in children and during emergencies or initial treatment of ESKD. In IPD, a special catheter with multiple holes is inserted into the patient’s abdomen through which a special solution called the dialysate is infused into the abdominal cavity or peritoneal space. The dialysate absorbs waste products and excess fluids from the patient’s blood. After some time, the fluid is drained and the process is repeated several times in a day.
- IPD lasts for a period of 24- 36 hours and about 30 to 40 liters of dialysate solution is used up during the treatment.
- IPD is repeated at short intervals of 1 -3 days, as per the need of the patient.
2. Continuous Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis (CAPD) What is CAPD?
CAPD means :
C – Continuous: The process is uninterrupted (treatment without stopping for 24 hours a day, 7 days a week).
A – Ambulatory: The patient can walk around and performroutine activities.
P – Peritoneal: The peritoneal membrane in the abdomen works as a filter.
D – Dialysis: The method of purification of blood.
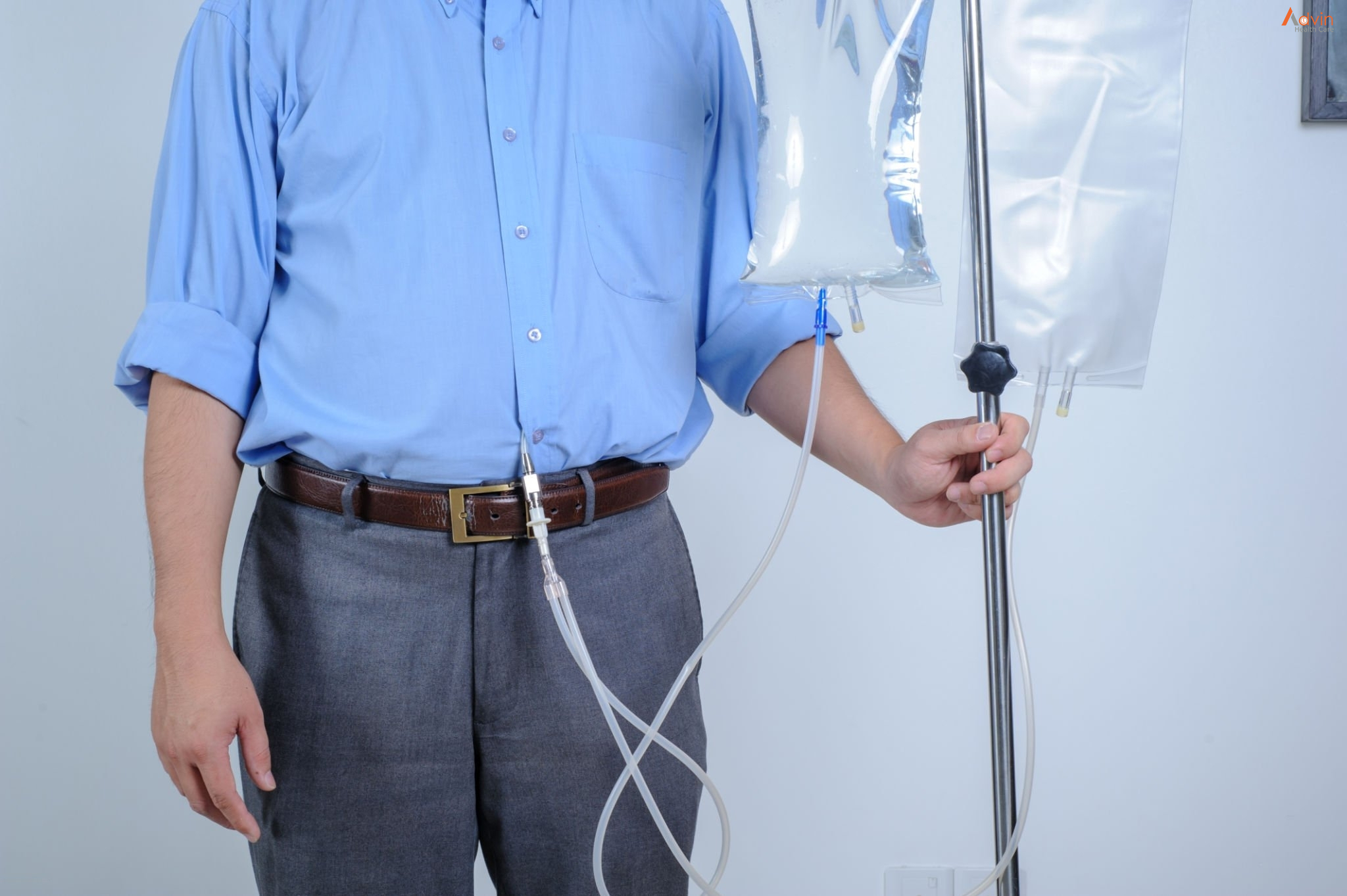
Continuous Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis (CAPD) is a form of dialysis which can be carried out by a person at home without the use of a machine. As CAPD provides convenience and independence it is a popular dialysis modality in many countries.
Process of CAPD :
CAPD catheter:The permanent access for peritoneal dialysis (CAPD catheter) is a soft thin flexible silicon rubber tube with numerous side holes. It is surgically inserted into the patient’s abdomen through the abdominal wall, about an inch below and to the side of the navel or belly button. The CAPD catheter is inserted about 10 to 14 days before CAPD starts. The PD catheter is the “life line” of CAPD patients, just as the AV fistula is to a patient on hemodialysis.
3. APD or Continuous Cycling Peritoneal Dialysis (CCPD):
Automated peritoneal dialysis (APD) or continuous cycling peritoneal dialysis (CCPD) is a form of PD treatment done at home using an automated cycler machine. The machine automatically fills and drains the PD fluid from the abdomen. Each cycle usually lasts for 1-2 hours and exchanges are done 4 to 5 times per treatment. The treatment lasts about 8 to 10 hours, usually at night, while the patient is asleep. In the morning, the machine is disconnected and 2 to 3 liters of PD fluid are usually left in the abdominal cavity. This fluid is drained the following evening before the next treatment is started. APD is advantageous since it allows the patient to go about regular activities during the day. Also, since the PD bag is connected and detached from the catheter only once a day, the procedure is more comfortable and carries less risk of peritonitis. However, APD may be expensive in some countries and can be a rather complex procedure for some patients.
What is PD fluid used in CAPD?
PD fluid (dialysate) is a sterile solution containing minerals and glucose (dextrose). Glucose in the dialysate allows removal of fluid from the body. Depending on the concentration of glucose, there are three kinds of dialysate available in India and in most areas worldwide (1.5%, 2.5% and 4.5%).The glucose concentration is selected for individual patients depending on the amount of fluid that needs to be removed from the body. Newer PD fluids are available in some countries which contain icodextrin instead of glucose. Icodextrin-containing solutions remove body fluids more slowly and are recommended for diabetic or overweight patients.
CAPD solution bags are available in different volumes ranging from 1000 to 2500 ml.