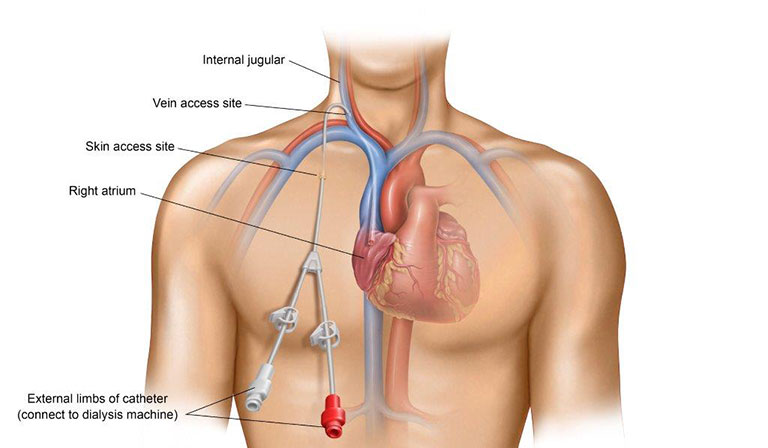
Permanent catheter
In Dr. Anil Patel’s kidney clinic, permanent catheters, also known as tunneled central venous catheters (CVC) or hemodialysis catheters, may be utilized for long-term vascular access in patients requiring chronic hemodialysis. Here’s how permanent catheters might be managed in his clinic:
Indication and Placement: Permanent catheters are typically indicated for patients who require long-term or permanent vascular access for hemodialysis due to the inadequacy of arteriovenous fistulas (AVF) or grafts, or if AVF or graft placement is not feasible. Dr. Patel assesses the patient’s vascular anatomy, comorbidities, and hemodialysis access needs to determine the appropriate type and location of catheter placement.
Insertion Procedure: Permanent catheters are inserted by trained interventional radiologists or vascular surgeons using a tunneled technique. The catheter is inserted into a central vein, such as the internal jugular or subclavian vein, and tunneled under the skin to exit at a separate site on the chest or neck. This tunneling technique helps reduce the risk of infection and provides stability for long-term catheter use.
Catheter Care and Maintenance: Dr. Patel and his team provide education to patients and caregivers on proper catheter care and maintenance to reduce the risk of complications, such as infection, thrombosis, or catheter dysfunction. This includes regular site inspection, dressing changes, and adherence to aseptic techniques during catheter manipulation.
Vascular Access Monitoring: Dr. Patel monitors the patency and function of permanent catheters regularly, assessing blood flow rates, monitoring for signs of infection or thrombosis, and troubleshooting any issues that may arise during catheter use. Regular monitoring helps ensure optimal catheter performance and patient safety.
Catheter Removal and Replacement: Permanent catheters may require removal and replacement periodically due to complications, such as infection, malfunction, or catheter-related thrombosis. Dr. Patel oversees the removal procedure and arranges for placement of a new catheter if ongoing vascular access is required.
Patient Education and Counseling: Dr. Patel educates patients and their families about the purpose of the permanent catheter, potential risks and benefits, and proper care techniques. Clear communication and patient education empower patients to actively participate in catheter management and reduce the risk of complications.
Multidisciplinary Collaboration: Permanent catheter management involves collaboration among various healthcare professionals, including nephrologists, dialysis nurses, interventional radiologists, infectious disease specialists, and wound care specialists. Dr. Patel coordinates care with these team members to ensure comprehensive management and optimal outcomes for patients with permanent catheters.
Overall, permanent catheters provide reliable long-term vascular access for hemodialysis in patients with chronic kidney disease, and their management in Dr. Anil Patel’s kidney clinic involves careful placement, diligent monitoring, patient education, and multidisciplinary collaboration to minimize complications and ensure safe and effective use.